-
2024-10-27 MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站党委成功举办学习贯彻党的二十届三中全会精神专题党课
-
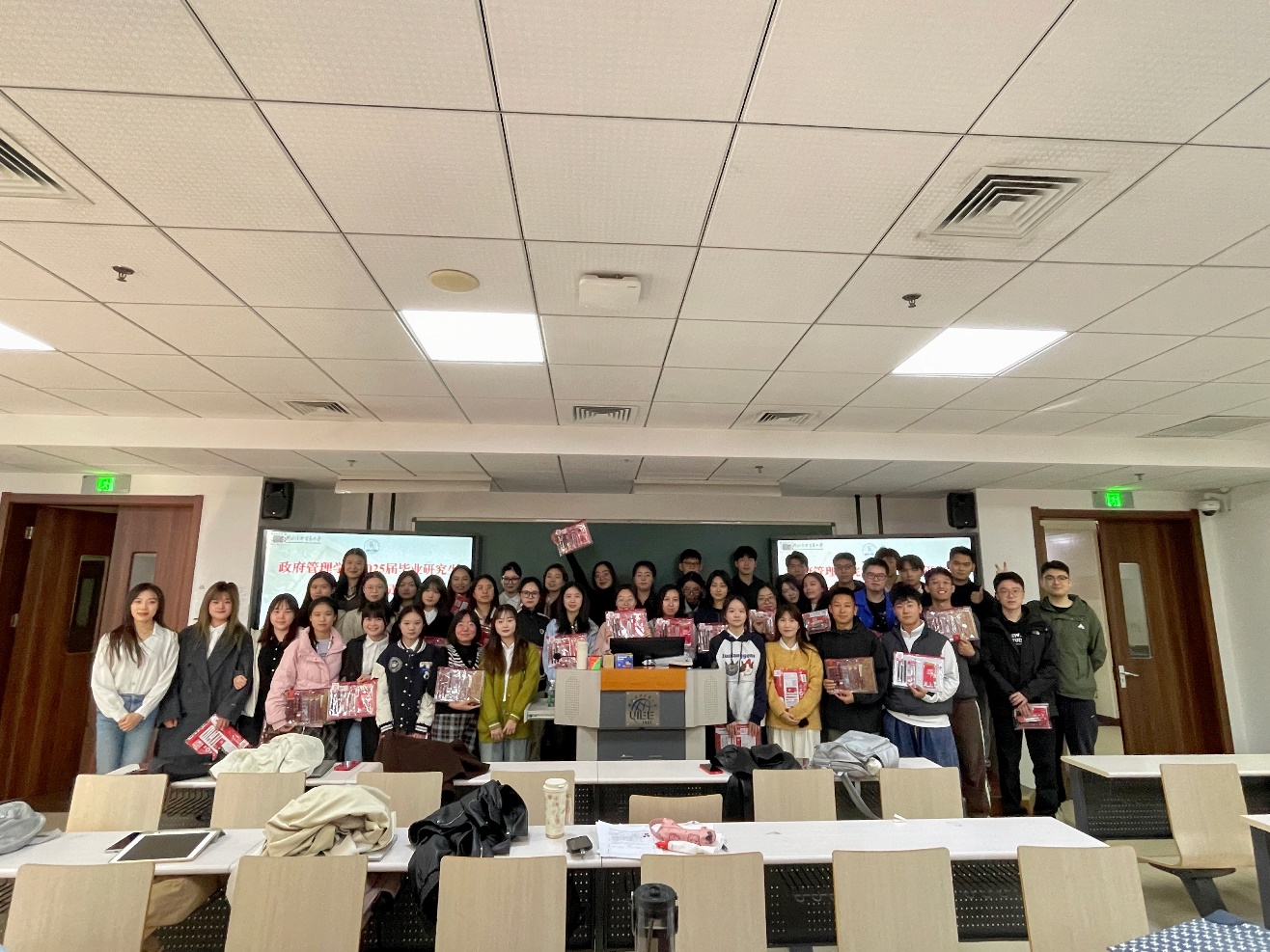
2024-10-27 MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站2025届毕业研究生就业创业动员大会顺利召开
-
2024-10-25 MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站召开2024年秋季学期期中全院大会
-

Qing Liu,Ruosi Lu,Stephen Teng Sun,Meng Zhang | Unintended workplace safety consequences of minimum wages
We investigate the unintended impact of minimum wage increases on workplace safety. Using establishment-level data from the United States and a cohort-based stacked difference-in-differences design, we find that large increases in minimum wages have significant adverse effects on workplace safety. Our findings indicate that, on average, a large minimum wage increase results in a 4.6 percent increase in the total case rate. Event study estimates show that this adverse effect persists in the medium run. Furthermore, we find a more salient effect for firms more likely to be financially constrained or subject to a higher labor market rigidity in firing workers. We provide suggestive evidence that small minimum wage increases might reduce injury rates, highlighting the potential heterogeneity in the impact of minimum wage changes. We do not find evidence that capital-labor substitution could be behind the findings.
-

Zhe Deng, Hanchen Jiang, Bo Fan, Xiao Tang | Balancing act: How do local governments use social media in crises?
Governments can benefit from social media usage in crisis management, but the amplified public scrutiny facilitated by social media may also impede crisis management and damage reputations. How governments balance such benefits and risks when using social media for crisis communication remains an open question. With a data set of epidemic statistics and social media posts of local governments across China during the first wave of COVID-19, we quantitatively investigate how the local crisis situations and coping resources influenced government usage of social media. Our analysis reveals that the first confirmed case in a city leads to a significant increase in government social media use. This effect is stronger in cities with more medical resources. In addition, the number of cumulative cases has an inverted U-shaped influence on government social media use. These findings suggest that governments value the importance of social media for crisis handling and reputation protection, adapting their communication strategies based on the crisis severity and their own capacities.
-

高照钰 | 《经济日报》:扩大服务业高水平对外开放
服务业发展水平是衡量现代社会经济发达程度的重要标志。2024年上半年,服务业增加值为349646亿元,占国内生产总值比重为56.7%。服务业对国民经济增长的贡献率为52.6%,在国民经济中的地位日益凸显。党的二十届三中全会对“完善高水平对外开放体制机制”“完善发展服务业体制机制”作出重要部署。在进一步全面深化改革过程中,以改革促开放特别是促进服务业扩大开放,是当前和今后一个时期的重点任务。
-

Biyun Zhu, Xuefei Li | Global policy diffusion as a socially constructed process
This study examines the diffusion of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network, focusing on the dynamics of four core diffusion mechanisms and reinterpreting them within a multi-agent framework. This approach enhances understanding of policy diffusion as a socially constructed process, emphasizing the heterogeneous pathways that various agents navigate within a single mechanism. Such variances are vital for grasping the complexities of why policies diffuse or fail, aspects that often escape traditional quantitative methods. In tracing the UNESCO Creative Cities Network’s diffusion from the Global North to South, we highlight UNESCO’s pivotal role in steering diffusion to reflect its evolving priorities; how cities appropriate the UNESCO Creative Cities Network to legitimize their policy goals and actions; the differing capabilities of cities from the Global North and Global South in negotiating and adopting such a global policy; and the tendency of global policies to diffuse among countries that are culturally proximate, as demonstrated by cultural distance index.
-
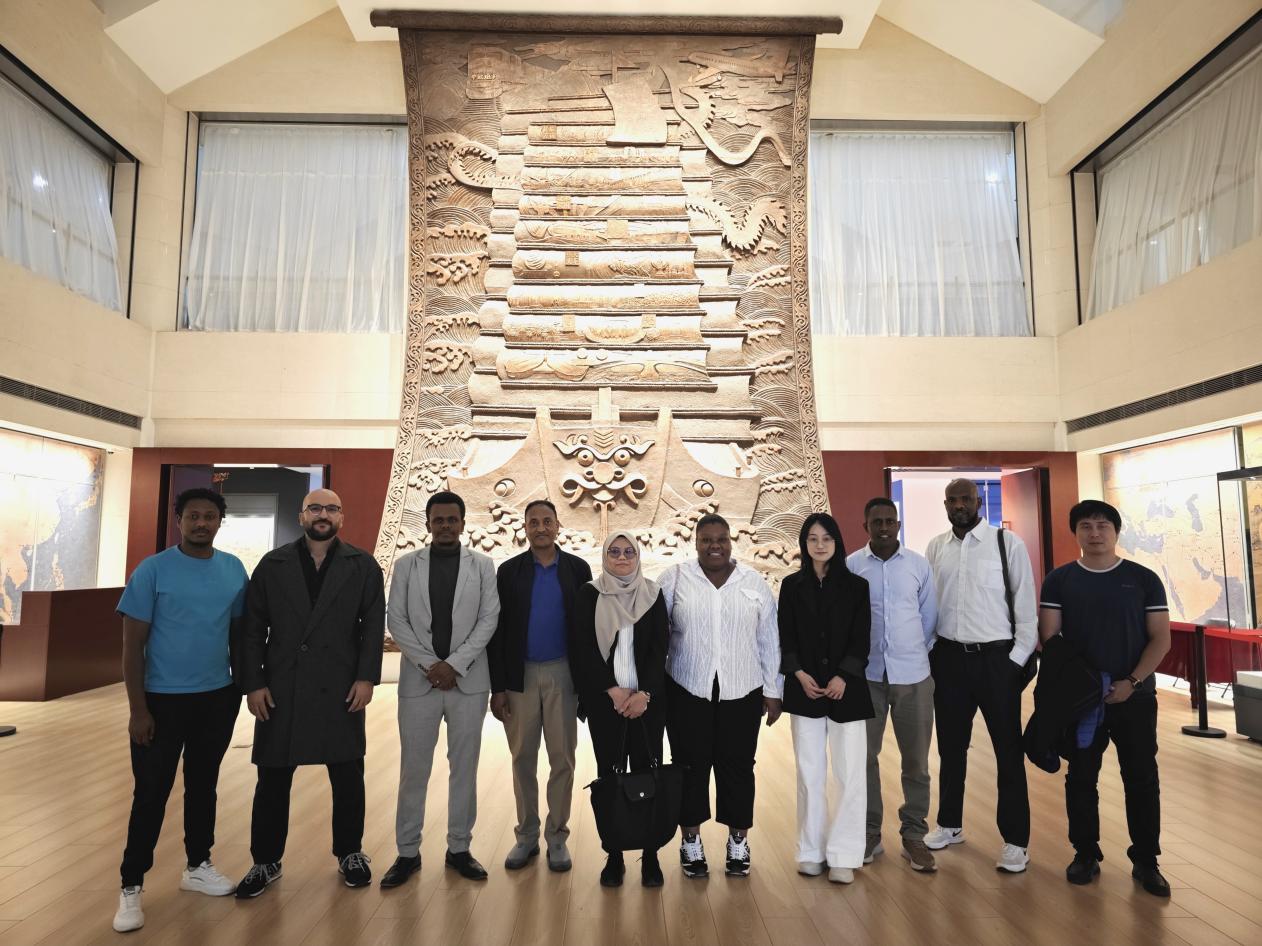 MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站2024级来华硕博留学生“文化月”活动暨校史馆探访为庆祝贸大来华留学生教育开展70周年,10月11日,对外经济贸易大学MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站博士留学生师生一行13人,在校史馆进行了一次深刻的文化探索之旅。留学生们不仅深入了解了中国贸易的发展历程,也亲身体验了贸大的独特魅力和深厚文化底蕴,标志着MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站2024级来华硕博留学生“文化月”的正式开幕。
MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站2024级来华硕博留学生“文化月”活动暨校史馆探访为庆祝贸大来华留学生教育开展70周年,10月11日,对外经济贸易大学MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站博士留学生师生一行13人,在校史馆进行了一次深刻的文化探索之旅。留学生们不仅深入了解了中国贸易的发展历程,也亲身体验了贸大的独特魅力和深厚文化底蕴,标志着MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站2024级来华硕博留学生“文化月”的正式开幕。 -
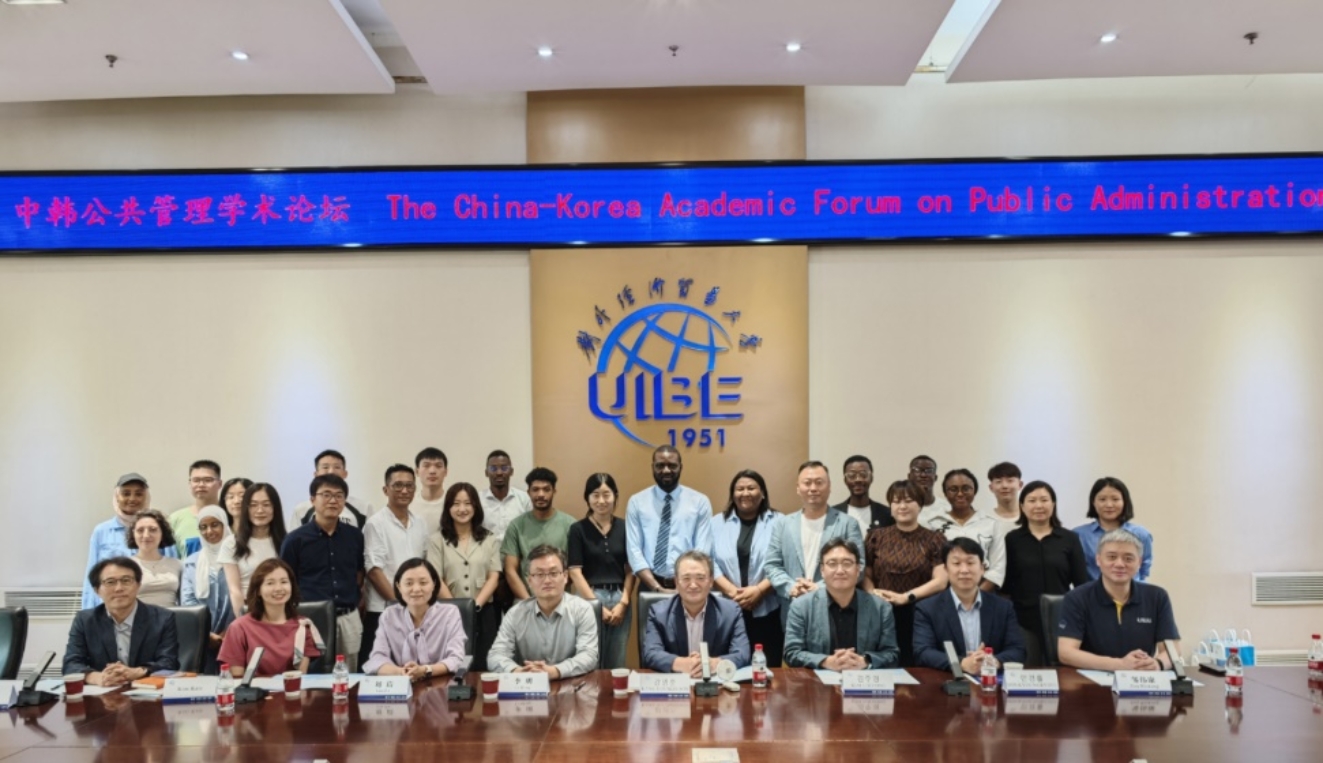 “中韩公共管理学术论坛·2024”成功举办2024年7月20日,在对外经济贸易大学迎来来华留学教育70周年、MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站建院50周年之际,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站在行政楼222室成功举办“中韩公共管理学术论坛·2024”。此次论坛,学院邀请到韩国国立济州大学师生代表,共同探讨和交流公共管理领域的最新研究成果和实践经验。论坛的核心目标是通过深入的学术交流,促进双方在公共管理领域的合作,提升中外留学生的趋同化管理水平,提高中韩硕博研究生的学术素养和研究能力。
“中韩公共管理学术论坛·2024”成功举办2024年7月20日,在对外经济贸易大学迎来来华留学教育70周年、MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站建院50周年之际,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站在行政楼222室成功举办“中韩公共管理学术论坛·2024”。此次论坛,学院邀请到韩国国立济州大学师生代表,共同探讨和交流公共管理领域的最新研究成果和实践经验。论坛的核心目标是通过深入的学术交流,促进双方在公共管理领域的合作,提升中外留学生的趋同化管理水平,提高中韩硕博研究生的学术素养和研究能力。 -
 MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站举办“在国际杂志发表:来自中国和丹麦公共管理及领导力研究的经验”讲座2024 年 6 月 12 日,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站(UIBE)成功举办主题为“在国际杂志发表:来自中国和丹麦公共管理及领导力研究的经验”的学术讲座。会议特邀丹麦奥胡斯大学管理系的教授 Anders Ryom Villadsen 作为主讲嘉宾。Anders Ryom Villadsen 教授是中丹研究中心的核心成员,2019 至 2023 年期间担任《公共行政研究与理论》(JPART)期刊副编辑。学院江汉臣副教授主持此次会议,学院教师、中外博士研究生参与此次会议。
MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站举办“在国际杂志发表:来自中国和丹麦公共管理及领导力研究的经验”讲座2024 年 6 月 12 日,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站(UIBE)成功举办主题为“在国际杂志发表:来自中国和丹麦公共管理及领导力研究的经验”的学术讲座。会议特邀丹麦奥胡斯大学管理系的教授 Anders Ryom Villadsen 作为主讲嘉宾。Anders Ryom Villadsen 教授是中丹研究中心的核心成员,2019 至 2023 年期间担任《公共行政研究与理论》(JPART)期刊副编辑。学院江汉臣副教授主持此次会议,学院教师、中外博士研究生参与此次会议。 -
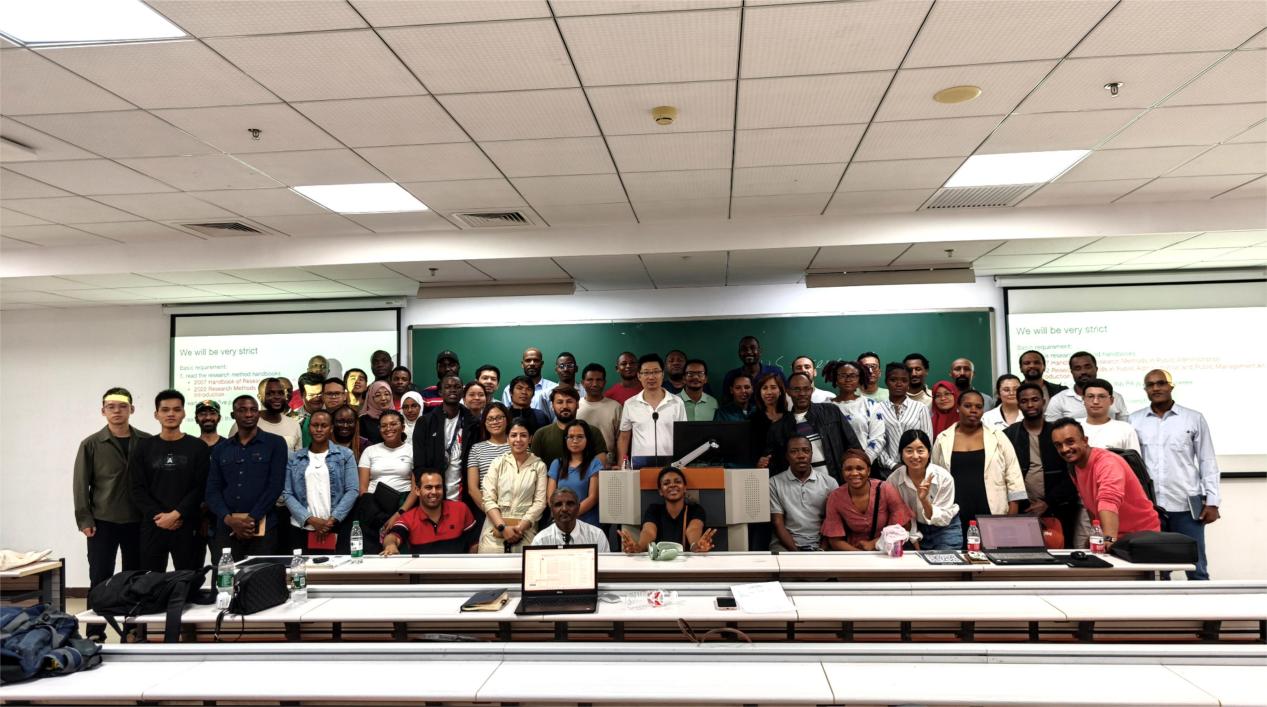 解析论文撰写要点,助力科研能力飞跃——MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站举办中外硕博科研能力系列讲座第二讲在不断追求学术卓越与国际化教育的大背景下,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站于5月30日成功举办了“发展与融合:来华留学生科研素养与能力提升”系列讲座的第二期。此次讲座以“Key Points in Writing a PhD Thesis: What You Should Do and What You Shouldn't Do”为主题,由行政管理系副教授江汉臣主讲,国际事务办公室主任徐萌萌主持,吸引了七十余名中外硕博研究生的积极参与。
解析论文撰写要点,助力科研能力飞跃——MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站举办中外硕博科研能力系列讲座第二讲在不断追求学术卓越与国际化教育的大背景下,MILAN米兰体育·(中国)官方网站于5月30日成功举办了“发展与融合:来华留学生科研素养与能力提升”系列讲座的第二期。此次讲座以“Key Points in Writing a PhD Thesis: What You Should Do and What You Shouldn't Do”为主题,由行政管理系副教授江汉臣主讲,国际事务办公室主任徐萌萌主持,吸引了七十余名中外硕博研究生的积极参与。